
Feedback should operate on four levels: 1. Provide opportunities for pupils to respond to feedback in the lesson in order to signal its importance and enable the teacher to recognise and celebrate progress.įeedback should answer three fundamental questions: Where are pupils going? (This is about their goals and is ‘feed up’) how are pupils going to get there? (This is ‘feed back’) and where to next? (This is ‘feed forward’). We do this by: greeting pupils at the door and using their names encouraging everyone to contribute and explicitly teaching speaking and listening skills modelling enthusiasm by being excited about teaching, ignoring anyone who advises ‘don’t smile till Christmas’ – even if this means we have to put on a act some days plan lessons on the premise of what pupils will think about rather than do – perhaps by framing lessons around a big question or hypothesis model a growth mindset ethos in which mistakes are positively welcomed and everyone gets better at everything with hard work and practice.Ĭreate a classroom in which taking risks and making mistakes is the default position and in which drafting and redrafting, improving work in response to feedback, is the norm. Here are my top ten tips for creating a positive learning environment which will stimulate pupils’ sensory memories:Ĭreate an ethos – delivered through words and actions – in which pupils feel welcomed, valued, enthusiastic about learning, engaged in their learning, eager to experiment, and rewarded for their hard work. Second, we need to make pupils think hard but efficiently.Īnd third, we need to plan for deliberate practice. In order to do this, we need to follow these three steps:įirst, we need to create a positive learning environment. In order to ensure our pupils learn, therefore, we need to stimulate their sensory memory, gain the attention of – and help them cheat – their working memory, and improve the strength with which information is stored in, and the ease and efficiency with which it can later be retrieved from, their long-term memory. Our long-term memory is where new information is stored and from which it can be recalled when needed, but we cannot directly access the information stored in our long-term memory – instead, this interaction between our sensory memory and our long-term memory occurs in the working memory.

Our sensory memory is made up of: what we see – this is called our iconic memory what we hear – this is called our echoic memory and what we touch – our haptic memory. DOI: 10.3389/ process of learning is the interaction between our sensory memory and our long-term memory. The duration of auditory sensory memory for vowel processing: Neurophysiological and behavioral measures. diseases-conditions/alzheimers-disease/in-depth/memory-loss/art-20046326 apa.org/ed/precollege/topss/lessons/memory.pdf Memory: A five-day unit lesson plan for high school psychology teachers. The neuroanatomical, neuropsychological and psychological basis of memory: Current models and their origins. A systematic review of the mismatch negativity as an index for auditory sensory memory: From basic research to clinical and developmental perspectives. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. Let’s look at how echoic memory works and how long it lasts, along with real-life examples. It also holds bits of audio information, which gives meaning to the overall sound.

The purpose of echoic memory is to store audio information as the brain processes the sound.
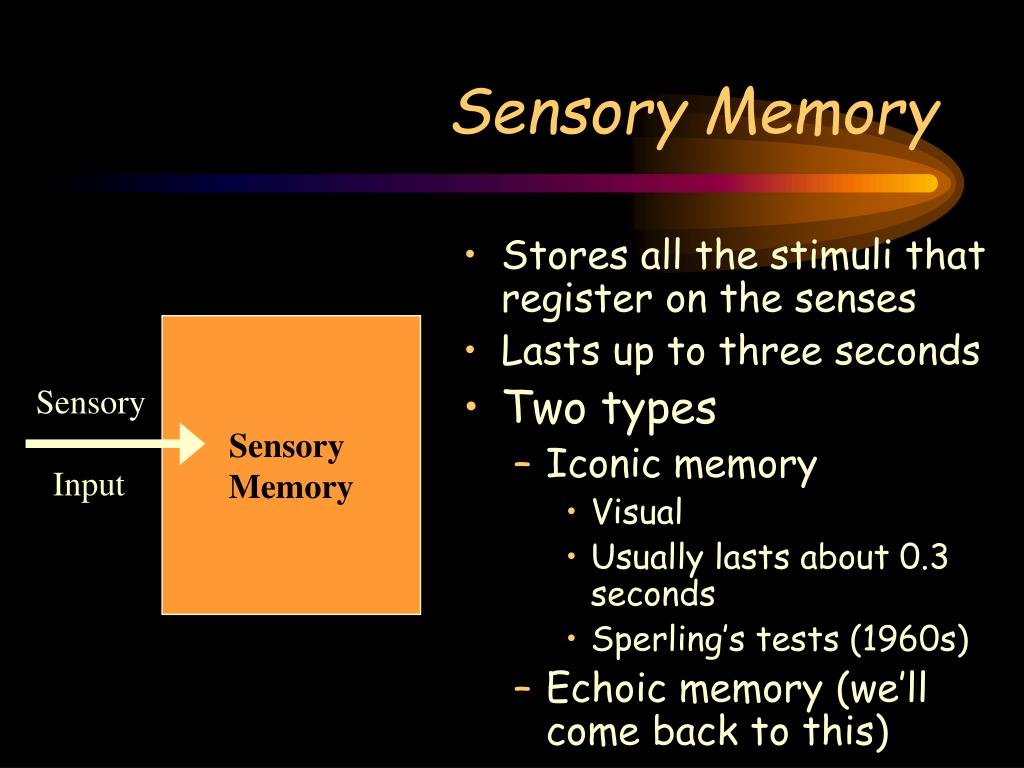
It’s a subcategory of human memory, which can be divided into three major categories: Echoic memory, or auditory sensory memory, is a type of memory that stores audio information (sound).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
